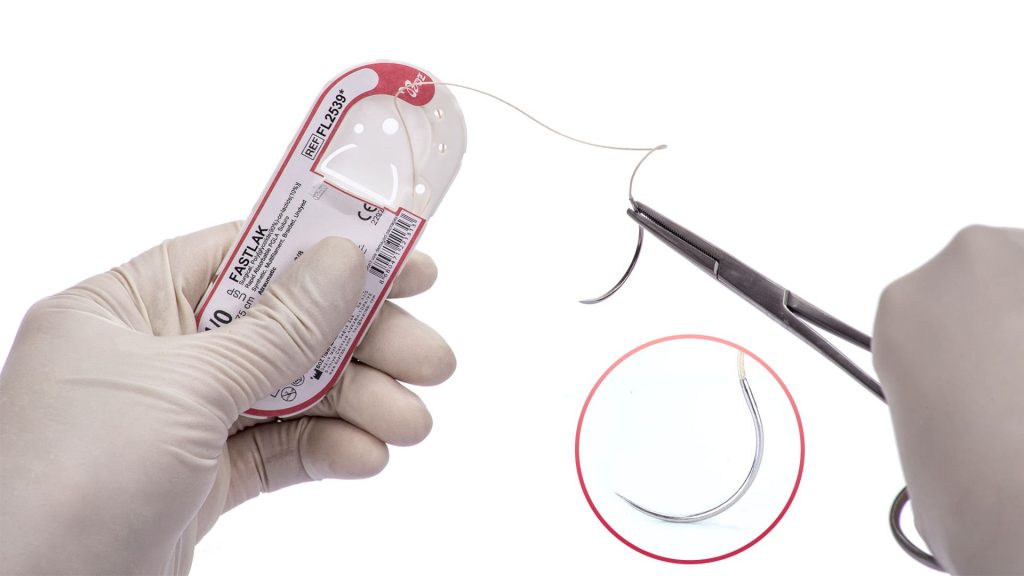
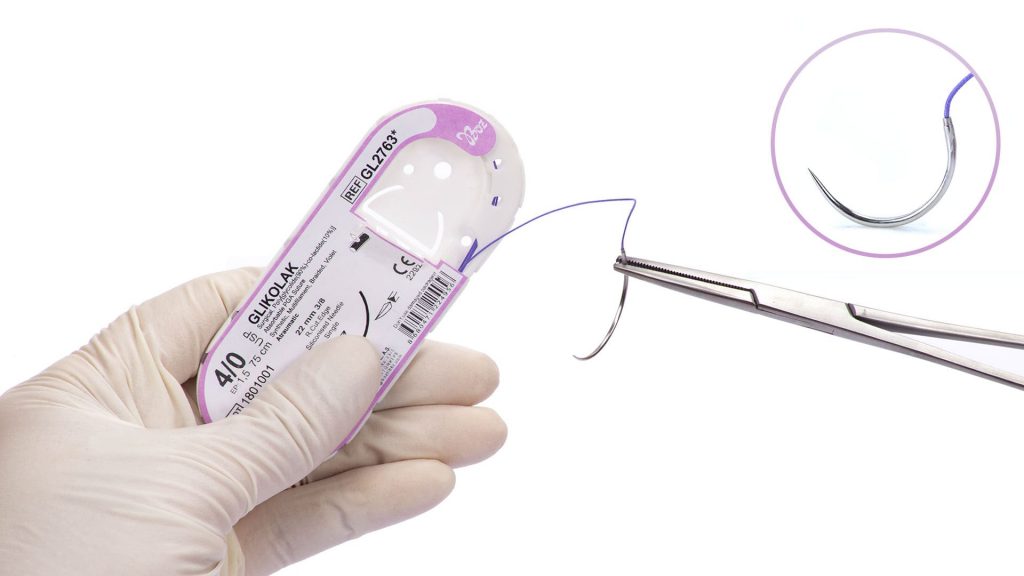
Polyglycolide-co-lactide (PGLA) Dental Sutures
Polyglycolide-co-lactide (PGLA) multifilament dental sutures used in oral, dental and maxillofacial surgery are divided into two as Fastlak fast absorbable and Glikolak absorbable sutures.
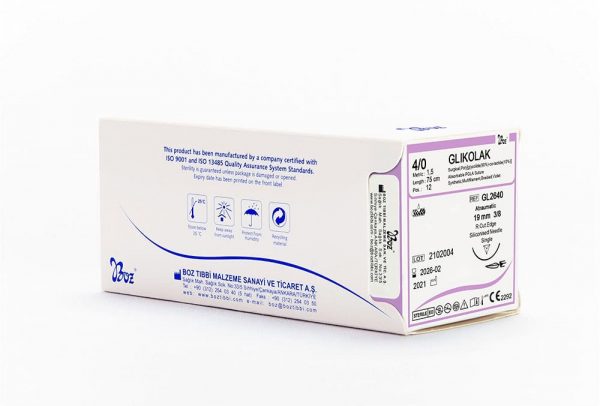
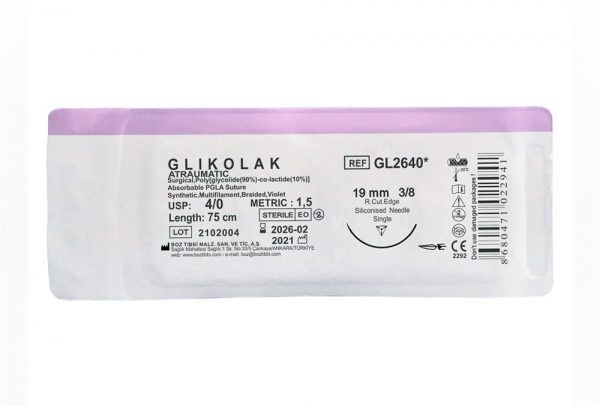
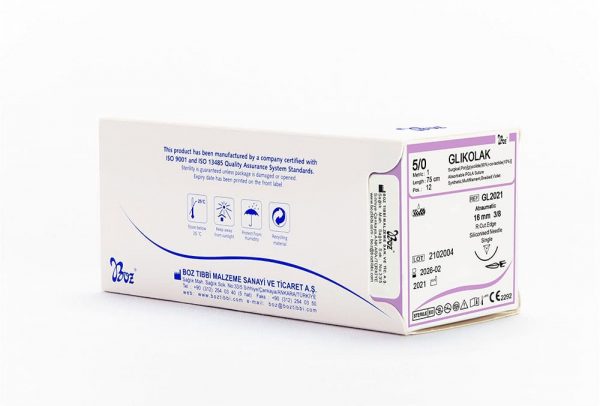
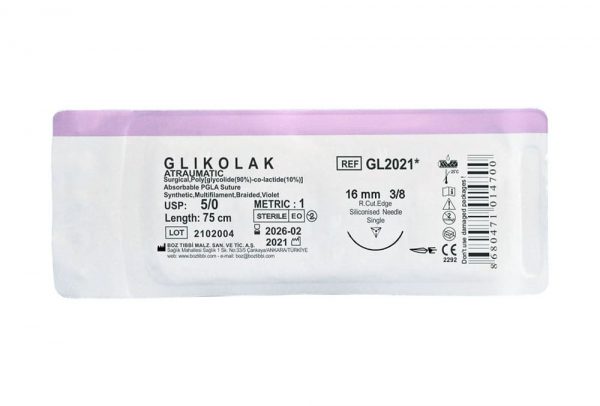
Absorbable PGLA dental sutures with 90% Glycolid and 10% L-Lactide (glycolic and lactic acid derivatives) chemical structure have flexible and synthetic structure. PGLA braided dental suture used as multifilament and absorbable suture by dentists in oral surgery are coated and manufactured with two colour variations as colourless (ivory) and violet. Polyglycolide-co-lactide (PGLA) sutures contains two types of products. These are Fastlak fast absorbable sutures and Glikolak absorbable sutures.
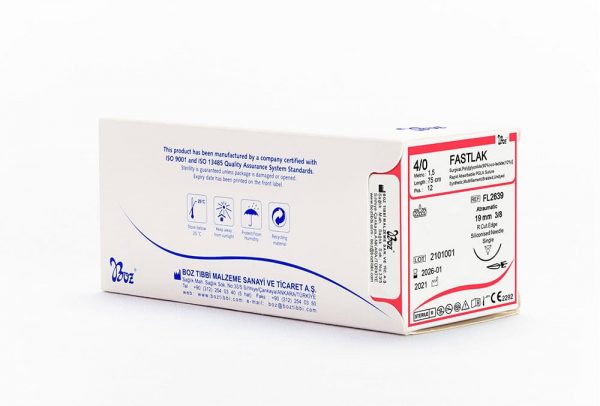
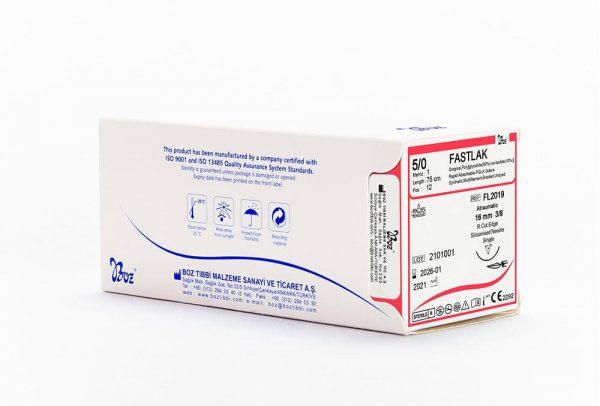
Fastlak fast absorbable sutures are sterilized with gamma, has calcium stearate, 30% Glycolic and 70% Lactide in its coating. Fastlak fast absorbable sutures are absorbed in 42 days and tissue support duration is 50% for the first week. Glikolak sutures are sterilized with EO (Ethylene oxide). Glikolak dental suture coating has Poly (Glycolid Lactide) (30/70) and calcium. Absorption duration is between 55-70 days and provides 75% tissue support on the 2nd week. These surgical sutures are commonly preferred as multifilament absorbable surgical sutures by dentists in oral, dental and maxillofacial surgery.
Structural Features For Fastlak
| FEATURES | Polyglycolide-co-lactide (PGLA) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Synthetic absorbable, coated, short term wound support and short term mass absorption. | |||
| Material | Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (30/70) glycolide 90% -lactide 10 % (PGLA) | |||
| Coating | Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (30/70) & calcium stearate | |||
| Structure | Braided | |||
| Colour | Beige (undyed) | |||
| Size | EP: 0.4 to 5 USP: 8/0 to 2 |
|||
| Tensile Strength Retention | 7 Days 50% – 10-14 Days 0% | |||
| Mass Absorption | 42 Days | |||
| Sterilization Method | Gamma Irradiation | |||
| Main Indication | Flep Implant Periodontal Intervention Embedded Tooth Extraction |
|||
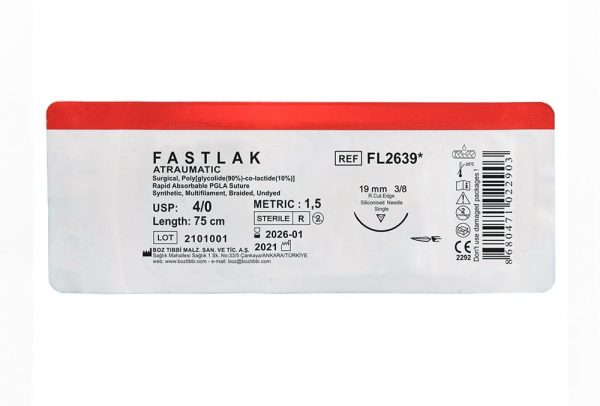
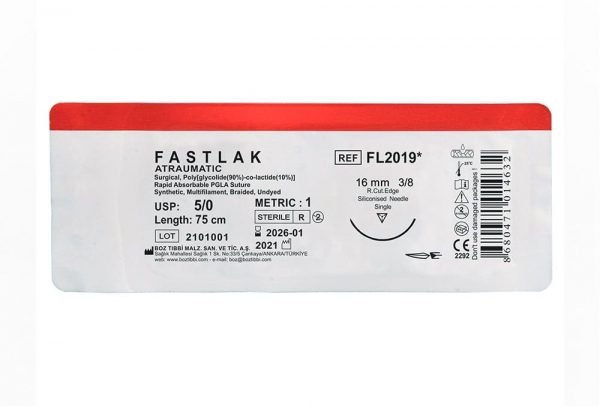
Fastlak Dental Suture Types and Sizes
| USP: 4/0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Needle Shapes and Descriptions | USP EP |
Lenght (cm) |
Unit Pcs | Color | ||
| 3/8 Reverse Cutting 19 mm |
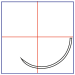 |
 |
3/0 1,5 |
75 | 12 | Undyed |
| USP: 5/0 | ||||||
| Needle Shapes and Descriptions | USP EP |
Lenght (cm) |
Unit Pcs | Color | ||
| 3/8 Reverse Cutting 16 mm |
 |
 |
3/0 1 |
75 | 12 | Undyed |
Absorbable surgical sutures (PGLA) Fastlak and Glikolak are preferred as colourless by the dentists in oral surgery. Other than that, the violet version is preferred to facilitate the surgical operation and when the suture must be visible on the tissues.
Structural Features For Glikolak
| FEATURES | Polyglycolide-co-lactide (PGLA) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Synthetic absorbable, coated, mid term wound support and mid term mass absorption. | |||
| Material | Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) glycolide 90% -lactide 10% (PGLA) | |||
| Coating | Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (30/70) & calcium stearate | |||
| Structure | Braided-Multifilament | |||
| Colour | Beige (undyed) or Violet (dyed) | |||
| Size | EP: 0.4 to 5 USP: 8/0 to 2 |
|||
| Tensile Strength Retention | 2. Week 75% | |||
| Mass Absorption | 55-70 Days | |||
| Sterilization Method | Ethylene Oxide Gas | |||
| Main Indication | Flep All-on-4 Cleft Palate Lip Apical Resection Periodontal Intervention Orthognathic Genioplasty Embedded Tooth Extraction |
|||
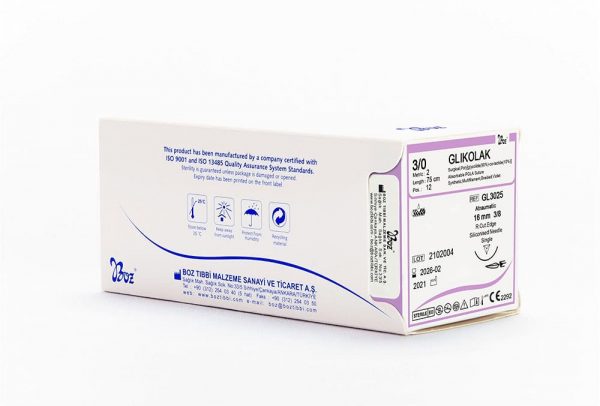
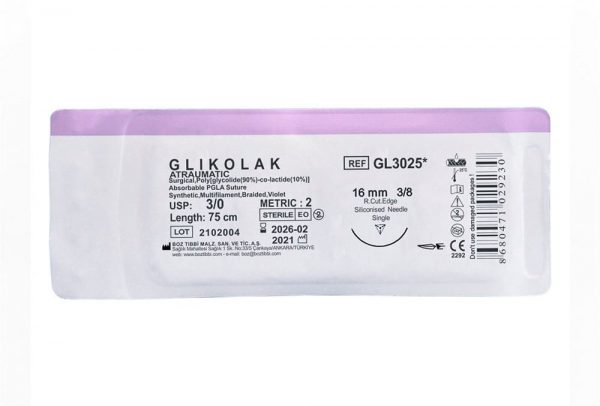
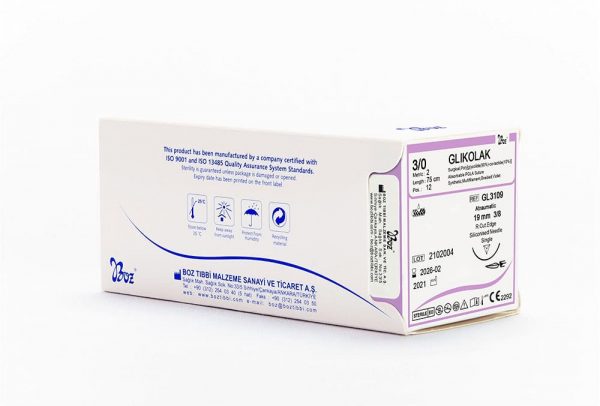
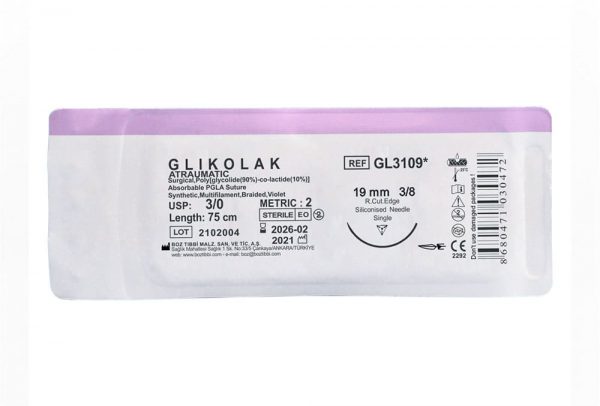
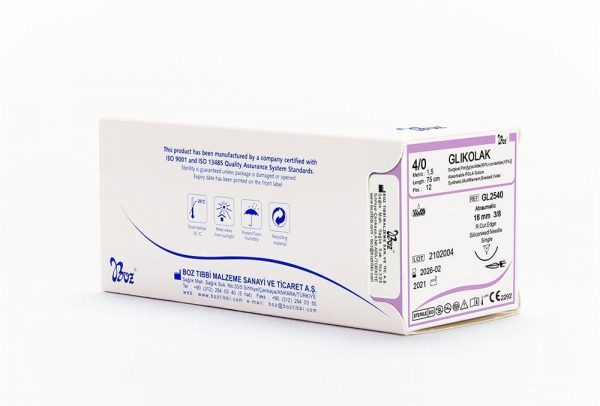
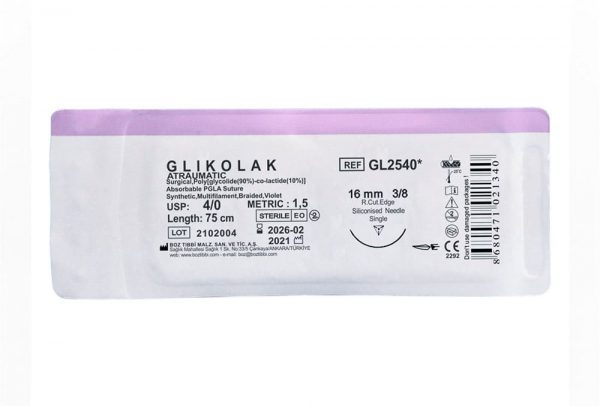
Glikolak Dental Suture Types and Sizes
| USP: 3/0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Needle Shapes and Descriptions | USP EP |
Lenght (cm) |
Unit Pcs | Color | ||
| 3/8 Reverse Cutting 16 mm |
 |
 |
3/0 2 |
75 | 12 | Violet |
| 3/8 Reverse Cutting 19 mm |
 |
 |
3/0 2 |
75 | 12 | Violet |
| USP: 4/0 | ||||||
| Needle Shapes and Descriptions | USP EP |
Lenght (cm) |
Unit Pcs | Color | ||
| 3/8 Reverse Cutting 16 mm |
 |
 |
3/0 1,5 |
75 | 12 | Violet |
| 3/8 Reverse Cutting 19 mm |
 |
 |
3/0 1,5 |
75 | 12 | Violet |
| USP: 5/0 | ||||||
| Needle Shapes and Descriptions | USP EP |
Lenght (cm) |
Unit Pcs | Color | ||
| 3/8 Reverse Cutting 12 mm |
 |
 |
3/0 1 |
75 | 12 | Violet |
Absorbable PGLA dental sutures used in oral, dental and maxillofacial surgery by dentists are preferred in implant operations to replace the missing tooth, all-on-4 operation which is another implant type, impacted tooth extraction, jaw tip cosmetic surgery called genioplasty, frenectomy to remove the frenulum tissue, to remove the inflamed area in the tooth root (apical resection), periodontal disease treatments, gum surgeries called flap, orthognathic surgery to eliminate jaw disorders, mucogingival interventions to correct gum-mucosa connection and to connect cleft lip.